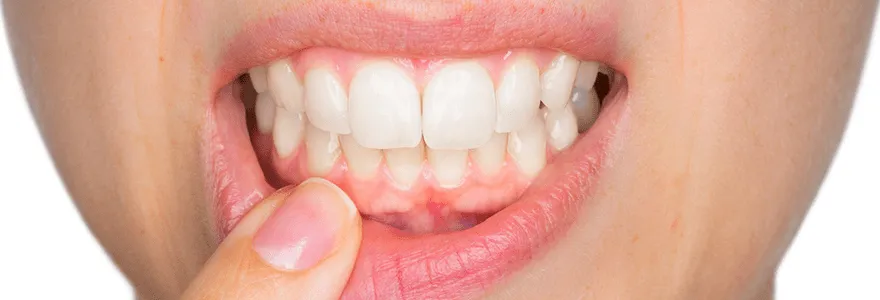
Those who faithfully brush their teeth each morning and night might feel as though they’re doing enough to achieve a healthy smile. However, even people with good oral care habits may hear from their dentist or dental hygienist that they have signs of gingivitis, an early form of gum disease. Arming yourself with a better understanding of gingivitis and tools to help fight it can help improve the health of your mouth and make your next dental visit a more positive experience. How to fight gingivitis: Gingivitis is a very common early form of gum disease that causes gums to become red, swollen and bleed easily during brushing or flossing. If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to a more serious form of gum disease known as periodontitis, which affects the tissues that surround and support the teeth and represents a major cause of tooth loss in adults. Fortunately, there are several ways you can protect yourself from gingivitis. Try these techniques between dental visits: Rinse, rinse, rinse! Using a mouth rinse is an important part of your overall oral care routine. Look for a rinse that protects against plaque and gingivitis. Give your mouth the time it deserves. Spending a little more time on your oral health is an easy way to help keep your smile in shape. Make sure to spend at least two minutes brushing, which should include 30 seconds of brushing each section of your mouth (upper right, upper left, lower right and lower left), both morning and night. Get in touch with your toothpaste. Not all toothpastes work the same, so choose one that protects against gingivitis. Check your gums regularly. Look for the warning signs of gingivitis and report them to your dentist right away. See your dentist for regular dental exams, and schedule a professional cleaning to remove stains and built-up tartar. Eat healthy foods for your oral health as well as your overall health. Eating excess sugar is one of the primary causes of dental problems. With the proper nutrients that come from healthy eating and proper oral hygiene, you can fight cavities and gingivitis. Don’t smoke. Smoking is a major contributor to dental problems and may cause oral cancer. Provided you look after them, your teeth and gums should be healthy. Brush twice daily, floss once a day and see your dentist regularly for optimum oral health.